Internationale Partnersuche
Innovation & Technologie Angebot
Inflammatory condition diagnosis and treatment
Country of Origin: Germany
Reference Number: TODE20200730001
Publication Date: 30 July 2020
Summary
A German university offers methods and compounds for preventing, diagnosing and treating an inflammatory condition based on antibodies. The method bears less risk of infections than conventional treatment. Furthermore thanks to the invention, for the first time danger-associated molecular pattern proteins can be blocked. The university seeks industrial partners for license agreements.
Description
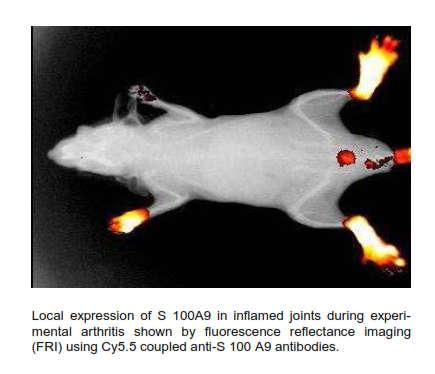
Uncontrolled inflammatory activation of the innate immune system plays an important role in infections, sepsis, septic shock, allergies, autoimmunity, as well as in cardiovascular diseases. Recently, so called danger-associated molecular pattern proteins (DAMPs) or alarmins attracted attention. They represent endogenous danger signals inducing inflammatory responses after being released from activated or necrotic cells. S100A8 and S100A9 belong to the group of DAMPs and promote inflammatory processes via activation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). They are expressed and re-leased at local sites of inflammation in all disorders mentioned above. A hallmark of this invention is the identification of the binding sites of S100A8 and S100A9 for TLR4.
Current therapies aimed at blocking TLR4 encompass an increased risk of infections, since such a therapy inevitably likewise blocks the response to bacterial products.
A German university offers a method that overcomes this problem. Their solution that specifically blocks the endogenous TLR4 ligands S100A8 and S100A9 has the advantage to inhibit inflammatory reactions by an approach that avoids these adverse effects. The specific release of these proteins at local sites of inflammation implicates a very selective molecular approach.
The German university’s invention comprises an antibody with specificity to an epitope of the human protein S100A9 or to an epitope of the human protein S100A8 involved in binding of TLR4.
Furthermore within this invention the use of such antibodies in the treatment or diagnosis of an inflammatory disorder is provided as well as an in vitro method of identifying a compound capable of inhibiting the formation of a complex between a peptide corresponding to one of the epitopes of S100A9 or the epitope of S100A8 and a TLR4 receptor.
Finally the invention also describes an in vitro method of identifying a compound capable of increasing the stability of a complex between a S100A8 protein and a S100A9 protein, where the two proteins are contacted in the presence of a compound suspected to affect the complex formation.
The university offers license agreements to providers of therapeutic products interested in taking up this invention for their portfolio.
Advantages and Innovations
The method described in this invention is the first ever approach to block a member of the DAMP family. Targeting S100A8 and S100A9 in mice has shown major anti-inflammatory effects in many inflammatory conditions.
A further advantage is that there is less risk of infections than with conventional therapies.
Stage Of Development
Under development/lab tested
Requested partner
The university offers license agreements
• Type of partner sought: Provider of therapeutic products
• Role of partner: Develop, produce and sell the invention
Cooperation offer ist closed for requests

